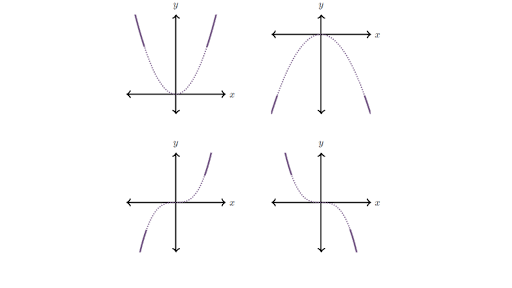
 Learn what the end behavior of a polynomial is, and how we can find it from the polynomial's equation. In this lesson, you will learn what the "end behavior" of a polynomial is and how to analyze it from a graph or from a polynomial equation.
Learn what the end behavior of a polynomial is, and how we can find it from the polynomial's equation. In this lesson, you will learn what the "end behavior" of a polynomial is and how to analyze it from a graph or from a polynomial equation. What is the end behavior of a function? Learn the end behavior rules and how to find the end behavior. See examples of the end behavior of different functions.
What is the end behavior of a function? Learn the end behavior rules and how to find the end behavior. See examples of the end behavior of different functions.